:: ParamList ::
exec oc.GetBlogInfo
@DomainName = '.com' ,
@Language = 'en-US' ,
@BusinessUnit = 'OP' ,
@BlogCategory = '__ALL__' ,
@BlogType = 'Research' ,
@BlogURL = 'water-flosser-peri-implant-mucositis-bunk-2020' ,
@Brand = '__ALL__' ,
WaterpikTM Water Flosser: Significantly More Effective at Reducing the Severity of Mucositis
The effect of adjunctive oral irrigation on self-administered oral care in the management of peri-implant mucositis. A randomized controlled clinical trial.
Objective
To evaluate the effect of adjunctive oral irrigation in addition to self-administered oral care on prevalence and severity of peri-implant mucositis.
Methods
Sixty (60) subjects completed this 12 weeks, randomized controlled, parallel clinical trial. Subjects were assigned to one of three treatment groups:
- Group 1 performed a standardized routine oral hygiene (ROH) consisting of brushing twice with and without toothpaste, interdental cleaning with device of choice.
- Group 2 performed ROH + water flossing with 50 ml water 1 x a day following tooth brushing and interdental cleaning in the evening.
- Group 3 performed ROH + water flossing with 50 ml 0.06% chlorohexidine (CHX) solution 1x a day following tooth brushing and interdental cleaning in the evening.
Clinical assessment was performed at baseline, 4, 8 and 12 weeks and included bleeding on probing (BOP), modified plaque-index (mPI) and mucositis-severity-score (MSS).
Results
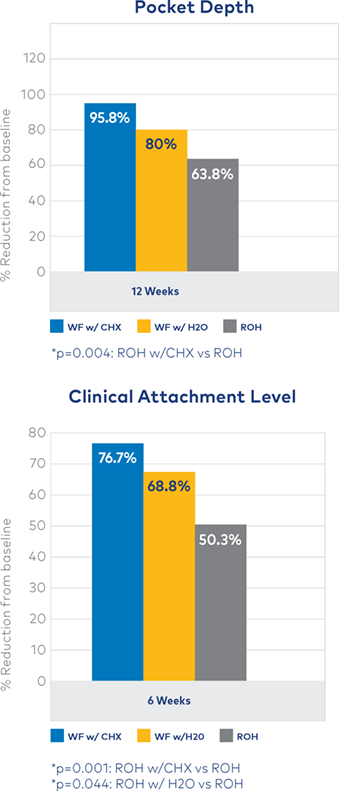
WaterpikTM water flosser with 0.06% provided the highest reductions and was significantly more effective than the ROH group for BOP and MSS. Both WaterpikTM groups reduced the mucositis-severity-score from moderate to mild.
There were no differences between the CHX irrigation and the water irrigation groups for any measurement.* The water irrigation was significantly more effective than the ROH group for adjusted mucositis-severity-scores at 12 weeks.
Conclusion
The WaterpikTM water flosser with water was safe and more effective at reducing the severity of mucositis compared to ROH (brushing and interdental cleaning). The addition of 0.06% CHX showed a greater improvement.
*The authors stated that no multiplicity correction was applied leading to exploratory rather than confirmatory conclusion. Based on the data provided, an increase in subjects from 20 to 50 would have shown a statistically significant difference between the water irrigation group and the ROH group. This would be consistent with other published studies.